The Essential Guide to EMS PCBA Manufacturing
Overview of EMS and PCBA
Electronics manufacturing services (EMS) provide outsourced design, testing, manufacturing, and distribution services for electronic components and assemblies. EMS companies allow clients to focus on their core competencies while the EMS provider handles production logistics and management.
PCBA (printed circuit board assembly) is at the core of electronics manufacturing. A printed circuit board (PCB) forms the backbone for electronic components. PCBA consists of soldering electrical components onto PCBs using surface mount technology (SMT) and/or through-hole technology (THT) components. The completed PCBA is then tested for functionality before shipment.
Choosing the right EMS provider for your PCBA needs depends on factors like capabilities, capacity, expertise, costs, and location. This guide provides a detailed overview of key aspects to consider when selecting an EMS provider for PCBA manufacturing.
Key Services Provided by EMS Companies
EMS companies form the backbone of electronics production across a range of industries like automotive, aerospace, telecom, medical devices and more. Here are some of the core services offered:
- PCBA manufacturing: Assembly of PCBs using SMT and THT processes. Testing and inspection of boards.
- PCB fabrication: Multi-layer PCB prototype builds and volume production. Includes sourcing PCB raw materials like laminates.
- Design support: Design for manufacturing (DFM) and design for testing (DFT) inputs to optimize manufacturing.
- Supply chain management: Procurement, inventory management and warehousing of components. Management of bills of materials (BOMs).
- Logistics: Warehousing, shipping and distribution of completed products. Managing reverse logistics.
- Aftermarket support: Repairs, refurbishment, spares management, obsolescence mitigation.
- Regulatory compliance: Support for certifications like ISO, IATF 16949 etc. Field failure analysis and reporting.
Choosing an EMS partner with strong capabilities across this range of services ensures a smoother production cycle.
Key Factors in PCBA Manufacturing
PCBA production requires expertise across a diverse set of domains. Here are some key factors to evaluate an EMS provider on:
1. Manufacturing Capabilities
- Breadth of SMT capabilities: 0201 components, microBGAs, 0.3mm pitch sizes etc.
- Fine pitch PCB capabilities.
- Complex assembly: multi-plane stacking, press fits, odd form factors.
- Flexible/rigid-flex PCB assemblies.
- Thermal management of high power boards.
- Conformal coating, potting and encapsulation.
- Variety of test/inspection processes.
2. Quality Processes
- IPC standards certifications.
- Statistical process controls.
- Process failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA).
- Traceability systems.
- Corrective action and continuous improvement.
3. Supply Chain Management
- Long-term preferred supplier agreements.
- Component engineering.
- Inventory management systems.
- Supply chain logistics and lead time reduction.
4. Tooling and Machinery
- SMT equipment types, speed, downtime and changeover times.
- Automated optical inspection (AOI).
- In-circuit and functional testing capabilities.
- X-Ray inspection systems.
Key Considerations for EMS Selection
Selecting the right EMS partner goes beyond assessing manufacturing capabilities. Here are some additional factors to evaluate:
Total Costs
- Upfront NRE charges.
- Unit pricing based on volumes.
- Test, inspection and ancillary costs.
- IP protection and IT infrastructure expenses.
- Cost reduction roadmaps and continuous improvement.
Technical Expertise
- Industry experience within niche verticals.
- Engineering support for DFM/DFT and product development.
- Obsolescence management and lifecycle extension services.
Quality and Compliance
- Quality certifications like ISO 13485, IATF 16949 etc.
- ITAR registration and controls where required.
- Reliability and defect rate track records.
- Warranties and repair/replacement support.
Customer Service
- Response time and communication platforms.
- Program management and customer reviews.
- Issue escalation processes.
- Shipment inspection support.
- Aftersales repair and technical assistance.
Location
- Proximity to end markets for quicker logistics.
- Infrastructure security and business continuity plans.
- Alignment of engineering and manufacturing teams.
Defining Requirements for an EMS PCBA Project
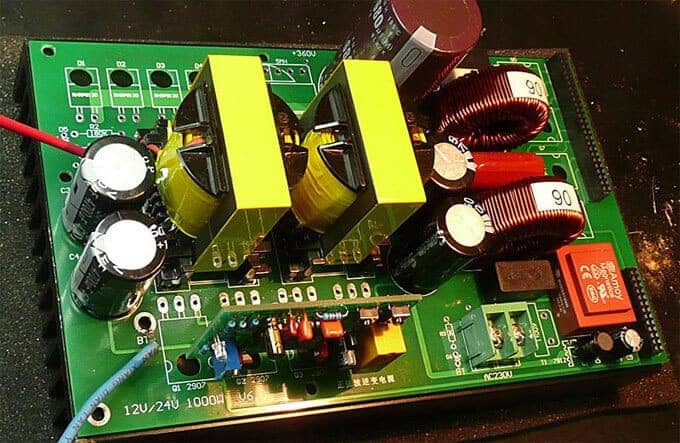

Kickstarting an EMS engagement requires clearly defining product requirements, specifications and expectations. Areas to provide detailed inputs on:
Product Specifications
- End product datasheets and technical manuals.
- Version control documents indicating changes.
- Regulatory standards compliance needed.
- Qualification testing expectations and standards.
- Reliability targets like MTBF.
Design Package
- Complete sensor, enclosure and subsystem designs.
- Gerber files for PCBs.
- 3D models and mechanical drawings.
- PCB footprints, schematics, layouts, BoMs etc.
- Design safeguards against counterfeiting.
Test Specifications
- Product validation, verification and acceptance testing.
- Inspection processes to be implemented.
- Quality assurance (QA) audits required.
- Qualification and lot acceptance criteria.
Production Expectations
- Volumes needed and production ramp profiles.
- Target production costs.
- Packaging and labelling requirements.
- Service level agreements (SLAs) for yield, quality etc.
Effective requirements gathering minimizes misalignment and prevents delays in the project.
Optimizing Designs for Manufacturing
Design for manufacturing (DFM) principles allow optimizing PCB designs to avoid assembly issues, improve yields and reduce costs. Key areas of focus for DFM:
Component Selection
- Prefer standardized components that are readily available.
- Minimize variety of component package sizes and types.
- Avoid components prone to counterfeiting or obsolescence.
Placement Density
- Ensure adequate spacing between components for assembly and rework.
- Enable access for inspection and in-circuit testing.
PCB Layout
- Sufficient clearances between traces and pads.
- Include testpoints to enable quality checks.
- Ensure the layout is compatible with SMT assembly processes.
Heat Dissipation
- Incorporate thermal vias and interfaces needed for thermal management.
Testability
- Include testpoints, debug headers and interfaces needed for testing.
- Ensure accessibility of components for fixture engagement.
Early DFM analysis prevents expensive re-spins and modifications later on.
Key Stages in the EMS PCBA Process
Once product designs and specifications are finalized, EMS production progresses through several standard stages:
1. NPI and Prototyping
- Initial prototyping builds to validate design integrity.
- Design modifications based on feedback.
- Process optimization with risk production builds.
- Package validation testing.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Sourcing of components based on AVLs.
- Procurement of long-lead items.
- Vendor managed inventory systems.
3. SMT Assembly
- Solder paste stencil printing.
- High-speed component placement.
- Solder reflow soldering.
- Automated optical inspection (AOI).
4. Post SMT Processing
- Conformal coating and potting.
- Press-fit connectors, shields etc.
5. Box Build
- Manual insertion of connectors, cables etc.
- Assembly and integration of sub-systems.
- Enclosure assembly.
6. Testing and QA
- In-circuit testing, boundary scan etc.
- Burn-in testing.
- Manual visual inspection.
- Functionality testing.
- Quality assurance audits.
7. Packaging and Shipping
- Programming/configuration prior to shipment.
- Packaging in ESD safe materials.
- Labelling and serial number tracking.
Understanding this step-by-step process allows effective monitoring of progress and quality.
Key Considerations for Quality and Reliability
Electronics manufacturing requires stringent control of quality and reliability:
Process Controls
- Statistical process control monitoring of yields.
- Defect reduction through continuous improvement.
- Process control plans for every assembly step.
- Extensive operator training on process best practices.
Inspections
- Functional testing at multiple stages.
- ICT tests on each completed board.
- AOI after SMT for defects.
- X-Ray inspection of solder joints and BGAs.
- Burn-in testing at temperature and load.
Traceability
- Raw material certificates of compliance (CoC).
- Serial number tracking throughout assembly.
- Change management processes.
ESD Control
- ESD Certification to standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20.
- Extensive grounding, ionization, packaging.
- ESD training and compliance monitoring.
Quality Standards
- ISO 9001/13485 quality management certification.
- Zero defect quality targets.
- 8D problem resolution processes.
Thorough quality control is key to preventing field failures and reliability issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are some key benefits of outsourcing PCBA manufacturing to an EMS provider?
Some benefits include:
- Access to advanced manufacturing equipment and expertise without major capital investment.
- Ability to scale production rapidly based on demand.
- Management of complex supply chains.
- Support for product design and testing.
- Continuity of production with global facilities.
Q2: What types of components are used in PCBA?
PCBAs use two main types of components:
SMT components: Chips, resistors, capacitors etc. mounted directly on board surfaces.
Through Hole components: Connectors, switches, relays mounted by inserting leads into holes.
Additional parts like cables, shields and heat sinks are also used.
Q3: How are PCB assemblies tested?
Testing procedures include:
- In-circuit tests (ICT) to check individual components.
- Functional testing simulating product operation.
- Burn-in testing under temperature or vibration.
- Automated optical and x-ray inspection.
- Environmental stress tests for qualifications.
- Boundary scan and flying probe testing.
- Manual visual inspection.
Q4: What types of documentation are shared for PCBA manufacturing?
Typical documentation includes:
- Gerber files of PCB designs.
- Bill of materials (BOMs) with component details.
- Mechanical drawings, datasheets and models.
- AVLs and component specifications.
- Product assembly and test procedures.
- Regulatory compliance requirements.
Q5: How can EMS providers assist with optimizing BOM costs?
Strategies include:
- Component engineering to source cheaper equivalents.
- Custom packaging with suppliers to get volume discounts.
- Design feedback to eliminate unnecessary components.
- Utilizing component inventory across customers.
- Cost reduction through continuous improvement.



0 Comments