In the world of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, FR4 is a widely used and widely recognized material for producing high-quality and reliable PCBs. This epoxy-based laminate material has become an industry standard due to its exceptional properties and versatility in various electronic applications. Understanding the characteristics and advantages of FR4 PCBs is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in the development and production of electronic devices and systems.
Introduction
FR4, also known as flame-retardant type 4, is a composite material consisting of woven fiberglass reinforced with an epoxy resin. This combination of materials provides a robust and durable substrate for the fabrication of printed circuit boards, which are essential components in virtually every electronic device and system.
What is FR4?
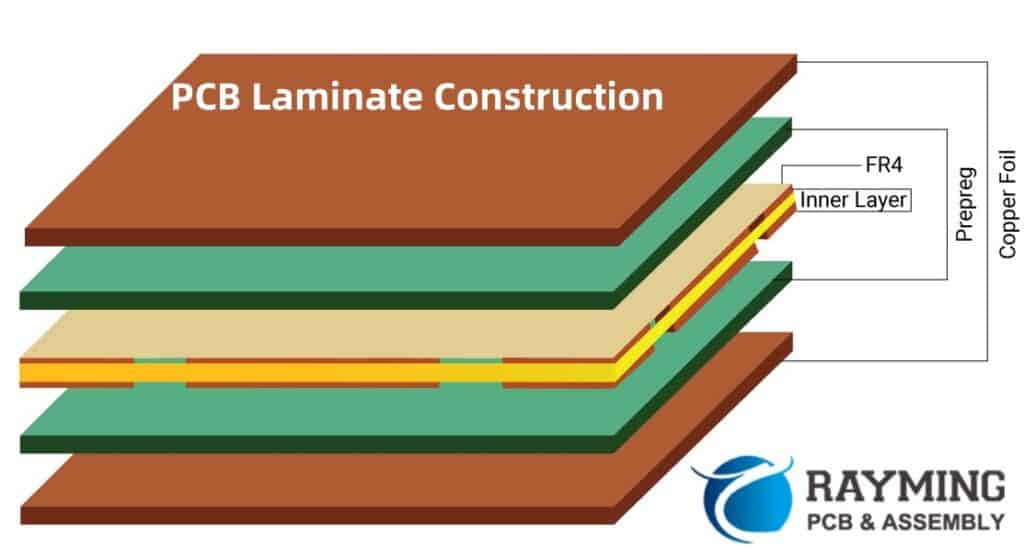
FR4 is a type of epoxy-based laminate material that is widely used in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. It is classified as a flame-retardant material due to its ability to resist and minimize the spread of fire, which is a critical safety feature in electronic applications.
The key components of FR4 are:
- Woven Fiberglass: The woven fiberglass cloth provides structural reinforcement and mechanical strength to the laminate material. It consists of interwoven strands of fine glass fibers, which are highly resistant to temperature and chemical exposure.
- Epoxy Resin: The epoxy resin serves as the binding agent, holding the fiberglass cloth together and providing electrical insulation properties. The epoxy resin is a thermoset polymer that cures and hardens into a rigid, cross-linked structure when subjected to heat and pressure.
- Flame Retardant Additives: To meet the flame-retardant requirements, FR4 incorporates specific additives, typically brominated compounds, which help inhibit and slow the spread of fire in case of exposure to high temperatures or open flames.
The combination of these components results in a rigid, durable, and fire-resistant material suitable for a wide range of PCB applications.
Properties and Advantages of FR4 PCBs
FR4 PCBs offer numerous advantages that have contributed to their widespread adoption in the electronics industry:
- Mechanical Strength and Rigidity: The woven fiberglass reinforcement and cured epoxy resin provide FR4 PCBs with excellent mechanical strength and rigidity. This property makes FR4 PCBs resistant to physical stress, vibrations, and impacts, ensuring durability and reliability in various operating environments.
- Electrical Insulation: The epoxy resin in FR4 PCBs acts as an excellent electrical insulator, minimizing the risk of short circuits and ensuring reliable signal integrity. This property is crucial for high-density PCB designs and high-frequency applications.
- Thermal Stability: FR4 PCBs exhibit good thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 130°C (266°F) or higher, depending on the specific grade and application requirements. This thermal stability is essential for PCBs used in high-temperature environments or applications involving power electronics.
- Flame Retardancy: As the name suggests, FR4 PCBs are designed to be flame-retardant, meeting industry standards for fire safety. This property is particularly important in applications where electrical components or devices may be exposed to potential fire hazards or high temperatures.
- Chemical Resistance: The epoxy resin and fiberglass composition of FR4 PCBs provides good resistance to various chemicals, solvents, and moisture, making it suitable for use in harsh environments or applications requiring chemical exposure.
- Cost-Effectiveness: FR4 PCBs are relatively inexpensive compared to other specialized PCB materials, making them an economical choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial and automotive electronics.
- Availability and Manufacturing Compatibility: FR4 is widely available and compatible with various PCB manufacturing processes, including etching, plating, and drilling. This availability and compatibility contribute to the ease of manufacturing and widespread adoption of FR4 PCBs.
Applications of FR4 PCBs
FR4 PCBs are used in a vast array of electronic applications across various industries, including:
- Consumer Electronics: FR4 PCBs are extensively used in consumer electronics products, such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, televisions, and home appliances, due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability.
- Industrial Electronics: In the industrial sector, FR4 PCBs are employed in control systems, automation equipment, instrumentation, and machinery, where durability and resistance to harsh environments are essential.
- Automotive Electronics: The automotive industry relies on FR4 PCBs for various electronic systems, including engine control units (ECUs), infotainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), owing to their thermal and mechanical stability.
- Telecommunications: FR4 PCBs are utilized in telecommunications equipment, such as routers, switches, and base stations, where reliability and signal integrity are critical factors.
- Medical Electronics: The medical industry often utilizes FR4 PCBs in diagnostic equipment, patient monitoring devices, and other medical instruments, benefiting from their flame retardancy and chemical resistance.
- Aerospace and Defense: FR4 PCBs find applications in aerospace and defense systems, including avionics, radar systems, and military electronics, where strict safety and reliability standards are required.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Embedded Systems: The growing demand for IoT devices and embedded systems has driven the use of FR4 PCBs in various applications, such as sensor nodes, gateways, and control systems, due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Design Considerations for FR4 PCBs
When designing and manufacturing FR4 PCBs, there are several considerations and best practices to keep in mind:
- Thermal Management: While FR4 PCBs offer good thermal stability, proper thermal management techniques, such as adequate copper area for heat dissipation and appropriate component placement, are essential for high-power or high-temperature applications.
- Trace Spacing and Clearance: FR4 PCBs have specific design rules for trace spacing and clearance to ensure reliable signal integrity and prevent short circuits, especially in high-density designs or high-frequency applications.
- Layer Stackup and Impedance Control: In multi-layer FR4 PCBs, careful consideration of the layer stackup and impedance control is necessary to maintain signal integrity and minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Moisture Sensitivity: While FR4 PCBs exhibit good moisture resistance, prolonged exposure to high humidity or moisture can potentially degrade the material over time. Proper handling, storage, and packaging practices are recommended to mitigate this risk.
- Fabrication Limitations: FR4 PCBs have certain limitations in terms of minimum feature sizes, layer counts, and aspect ratios, which may vary depending on the specific manufacturing capabilities and design requirements.
- Environmental Considerations: While FR4 PCBs offer flame retardancy, the brominated compounds used as flame retardants have raised environmental concerns. Alternative flame retardant materials or halogen-free FR4 variants may be preferred in certain applications or regions with stricter environmental regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: What is the difference between FR4 and other PCB materials like CEM-3 or Rogers? A: FR4 is an epoxy-based laminate material, while CEM-3 and Rogers materials are specialized substrates designed for high-frequency or radio frequency (RF) applications. These materials offer superior electrical properties and better signal integrity at higher frequencies compared to FR4, but they are generally more expensive and have different mechanical and thermal characteristics.
- Q: Can FR4 PCBs be used in high-frequency or RF applications? A: While FR4 PCBs can be used in some high-frequency or RF applications, their performance may be limited due to factors such as dielectric losses and signal integrity issues at higher frequencies. For optimal performance in high-frequency or RF applications, specialized materials like Rogers or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) may be more suitable.
- Q: Are there different grades or types of FR4 PCBs available? A: Yes, FR4 PCBs are available in different grades or types, with variations in their properties and specifications. Common grades include standard FR4, high-temperature FR4 (FR4-HT), and halogen-free FR4 (FR4-HF), each with different thermal, electrical, and environmental characteristics to suit specific application requirements.
- Q: Can FR4 PCBs be recycled or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner? A: FR4 PCBs can be recycled through various processes, such as mechanical shredding and separation, or chemical processes to recover valuable materials like copper and fiberglass. However, the presence of brominated flame retardants in standard FR4 PCBs can pose environmental concerns during disposal or recycling, making proper handling and disposal practices essential.
- Q: Are there any limitations or drawbacks to using FR4 PCBs? A: While FR4 PCBs offer many advantages, they do have some limitations. These include relatively poor thermal conductivity compared to specialized materials like ceramics or aluminum, limited performance at higher frequencies, and potential environmental concerns related to the use of brominated flame retardants. Additionally, FR4 PCBs may not be suitable for applications requiring extreme temperatures or highly specialized electrical properties.
FR4 PCBs have become an industry standard due to their exceptional combination of mechanical strength, electrical insulation properties, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness. Their widespread availability, compatibility with various manufacturing processes, and ability to meet safety and reliability standards have made them a preferred choice for a wide range of electronic applications. While FR4 PCBs may have certain limitations, their versatility and proven track record make them a reliable and economical solution for many electronic products and systems.



0 Comments